How do human brains work?
Nerve cells are at the center of everything when it comes to brain functionality. A nerve cell neuron is a special biological cell that processes information. According to an estimation, there is a huge number of neurons, approximately with numerous interconnections. There are basically 4 parts of a neuron, then helps it to process and transfer information:
- Synapses: Synapse is the connection point of two nerve cells.
- Dendrites: They are tree-like branches, responsible for receiving the information from other neurons it is connected to. In another sense, we can say that they are like the ears of neurons.
- Soma: It is the cell body of the neuron and is responsible for the processing of information, they have received from dendrites.
- Axon: With this part, a cell transfers information to another cell (like wires).
Here is an image showing the connection of two neurons and their different parts.
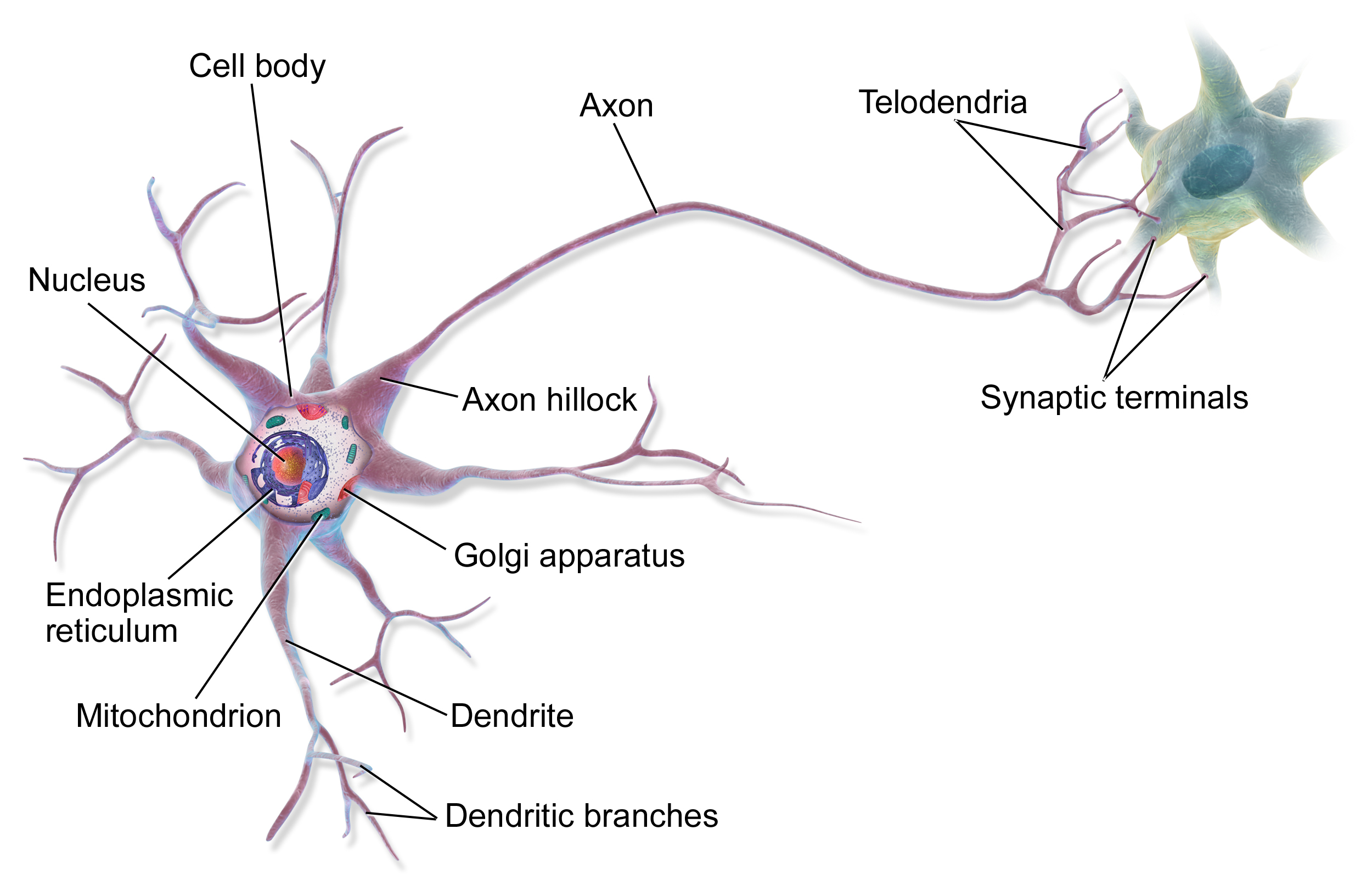
This is not a biology lesson, right? So why are we learning about brains? Because neural networks are nothing but brains created by humans. Below is the analogy in neural networks of what we have read about brains earlier:
- Synapses are weights in an artificial neural network (ANN).
- Dendrites are the input of a cell in ANN.
- Soma is a node or unit cell in ANN.
- Axon is the output of a cell in ANN.

