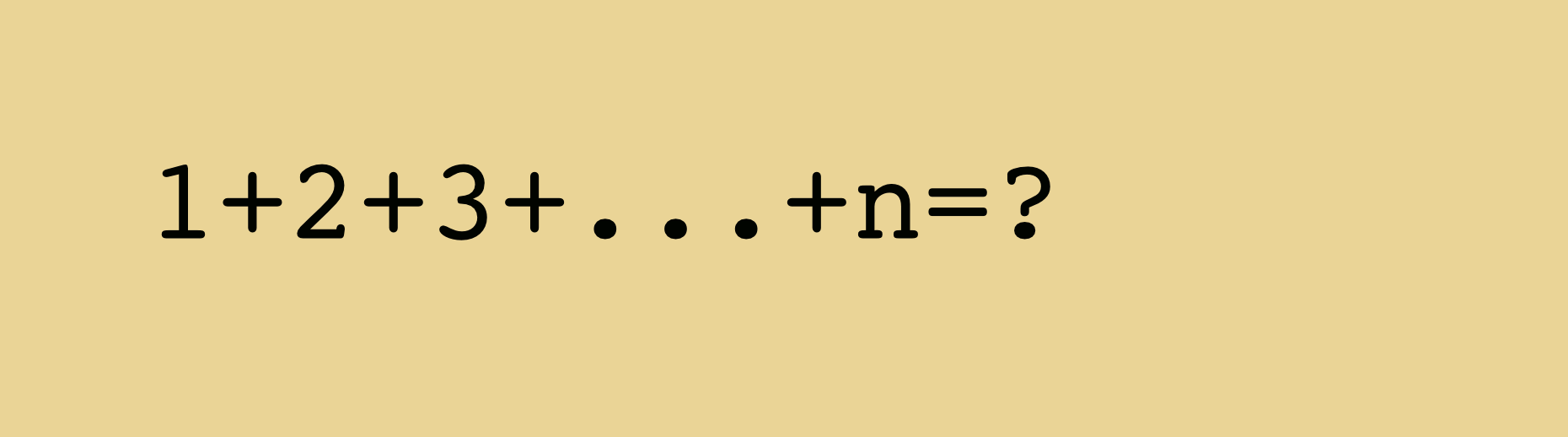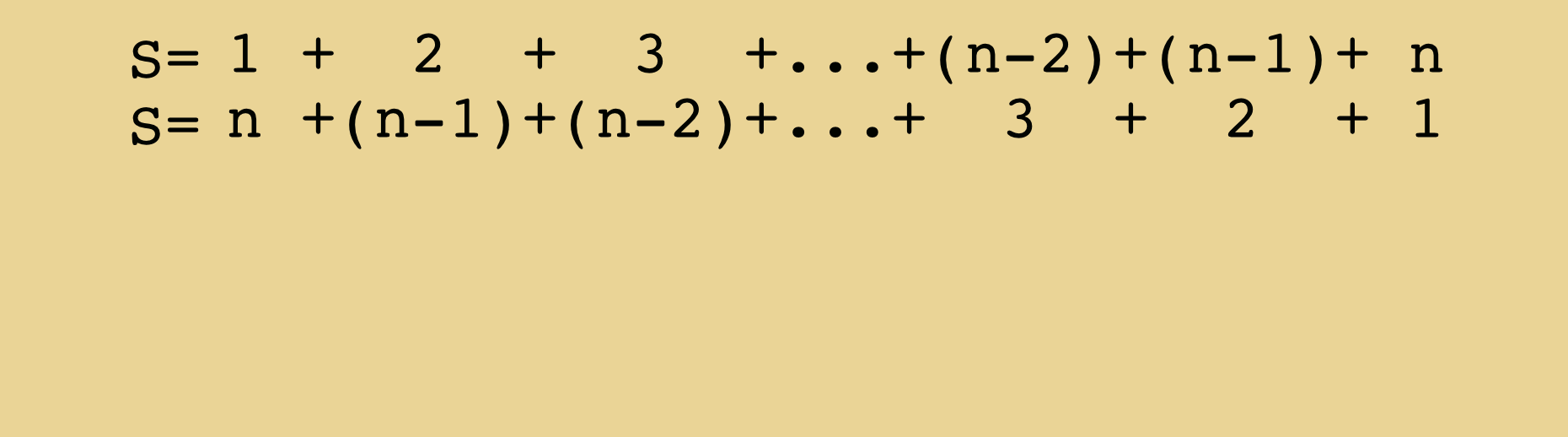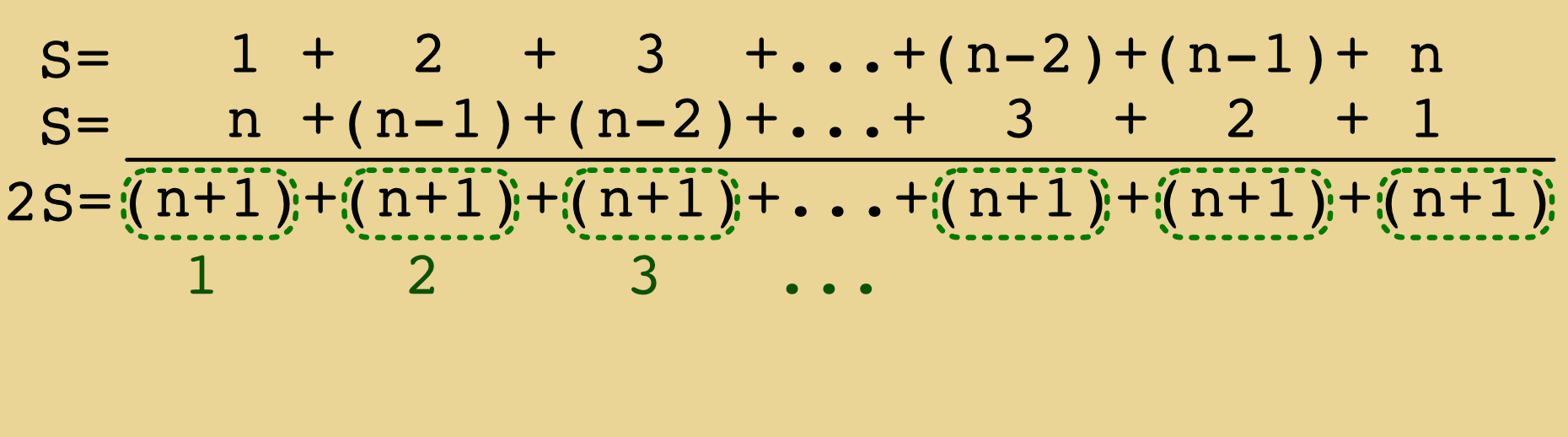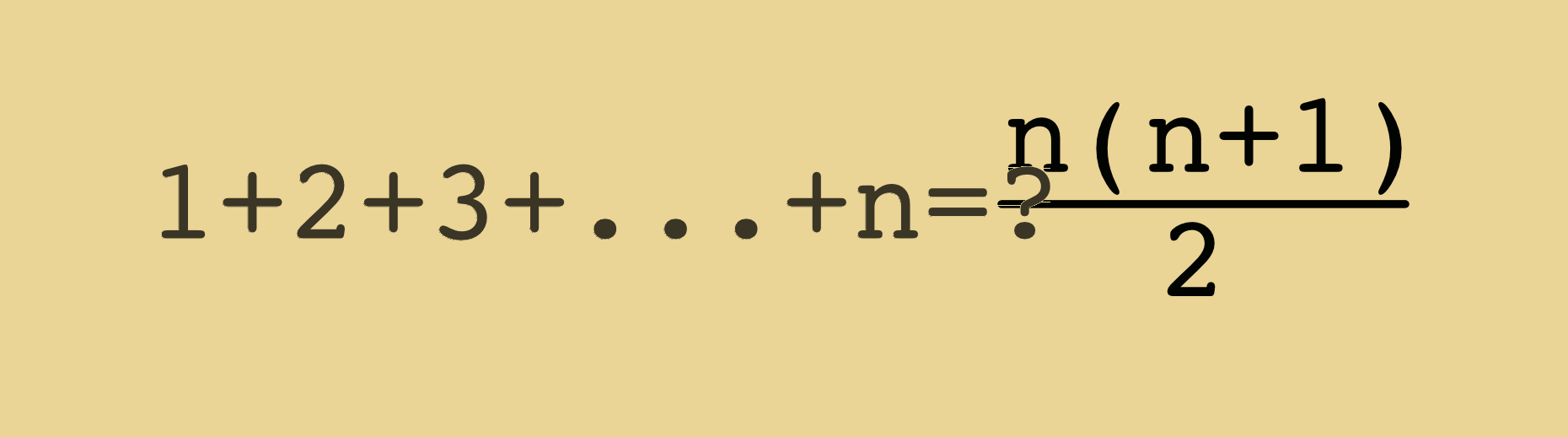- Essentials
- Specialties
- Nontechnical
- Personalized
- Generate a Custom Course 🪄
- Guided
- 60 Day Interview Crash Course


Medium Arrays
A basic linear data structure that holds a fixed number of containers to store data.

Section Menu
How do I use this section?

Cheat Sheet
- Quick summary: a collection that stores elements in order and looks them up by index.
- Also known as: fixed array, static array.
- Important facts:
- Stores elements sequentially, one after another.
- Each array element has an index. Zero-based indexing is used most often: the first index is 0, the second is 1, and so on.
- Is created with a fixed size. Increasing or decreasing the size of an array is impossible.
- Can be one-dimensional (linear) or multi-dimensional.
- Allocates contiguous memory space for all its elements.
- Pros:
- Ensures constant time access by index.
- Constant time append (insertion at the end of an array).
- Cons:
- Fixed size that can't be changed.
- Search, insertion and deletion are
O(n). After insertion or deletion, all subsequent elements are moved one index further. - Can be memory intensive when capacity is underused.
- Notable uses:
- The String data type that represents text is implemented in programming languages as an array that consists of a sequence of characters plus a terminating character.
- Time complexity (worst case):
- Access:
O(1) - Search:
O(n) - Insertion:
O(n)(append:O(1)) - Deletion:
O(n)
- Access:
- See also: